MOBILE ROBOTS AND DRONES

Mobile systems break when sensor timing and data transport get unreliable under real load. FPGA front-ends keep sensor streams aligned and move data predictably into the compute stack.
• Sensors stay in sync for stable camera/IMU/encoder fusion
• Data arrives predictably instead of dropping under peak load
• Low-latency preprocessing delivers time-consistent blocks to CPU/GPU
Typical Use Cases in Mobile Robotic Systems
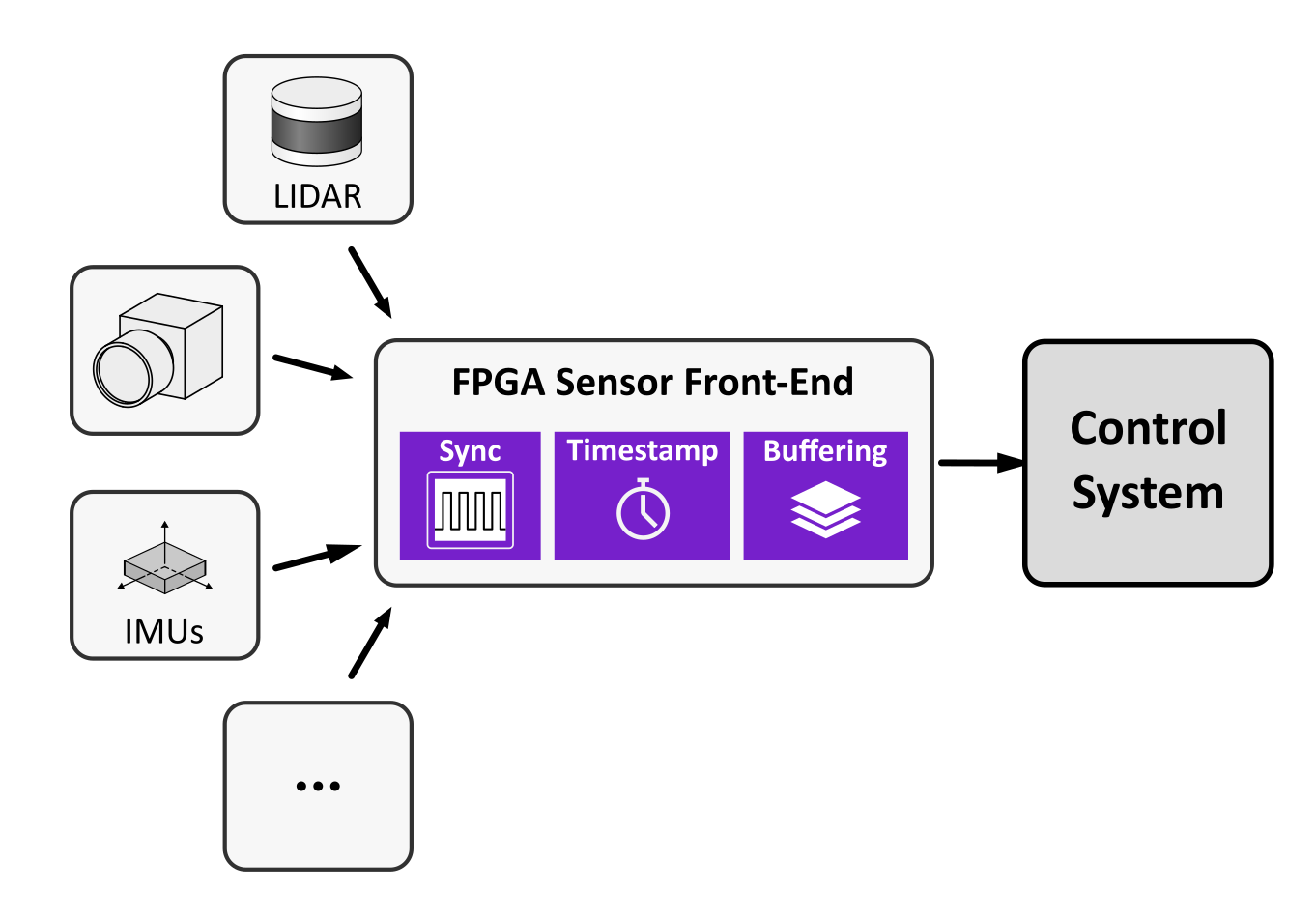
Perception Sensor Front-Ends for Robotics and UAVs
Perception stacks depend on sensor timing and alignment: camera/LiDAR/IMU data often arrives with inconsistent latency, weak synchronization, or fragile interface glue. FPGA-based sensor front-ends implement timing-accurate interfaces, deterministic timestamps and multi-sensor synchronization close to the source. This stabilizes downstream estimation and perception, and reduces integration risk when sensor links or timing constraints are non-trivial. Where needed, the sensor front-end (interfaces, clocking, analog/digital boundaries) is developed as a coherent subsystem rather than ad-hoc glue.
High-Rate Data Handling for Edge Perception
High-bandwidth sensors stress the data path long before algorithms become the bottleneck: buffering, framing and sustained throughput determine whether frames/packets arrive reliably under load. FPGA-based streaming pipelines provide lossless acquisition, deterministic buffering/backpressure handling and robust transport toward the compute platform. This keeps the perception system stable at sustained data rates and makes bandwidth limits measurable via built-in diagnostics. The result is a predictable, observable data backbone feeding SoC/GPU resources.
Real-Time Preprocessing for Navigation and Control
Navigation and control benefit from preprocessing that is time-deterministic and close to the signal source: alignment, filtering, gating and event detection should not depend on CPU scheduling. FPGA-based pipelines provide fixed-latency conditioning and feature extraction that reduces data volume and improves real-time behavior for downstream fusion and control loops. This is especially relevant when multiple sensors must remain phase-aligned or when triggers must be repeatable. The processing scope is typically kept modular and verifiable, focused on what improves timing and stability.
Failsafe & Supervision Logic in Mobile Systems
Mobile systems require fast, predictable reactions when something goes wrong: communication loss, sensor plausibility violations, limit breaches or actuator faults should lead to defined states independent of the main compute stack. FPGA-based supervision implements deterministic watchdogs, limit checks, interlocks and inhibit paths with well-defined behavior on reset and power events. This reduces common-mode failures between control software and safety reactions and makes fault handling reproducible during testing. The result is a clear separation between mission logic and a minimal, robust supervision layer.